WORLD WAR I
Published on 23 Oct 2025
World War I, also known as the Great War, was a global conflict that took place from 1914 to 1918, involving major powers and alliances across the world. It was triggered by a complex web of political, economic, and territorial tensions, and its far-reaching consequences profoundly impacted the course of history.
Characteristics of World War I
Product of Ultra-Nationalism, Imperialism, and Militarism: WW1 was triggered by intense nationalism, imperial ambitions, and the arms race among major powers, leading to mutual suspicion and distrust.
Division of the World into Major International Forces: At the turn of the century, distinct ideological forces emerged, competing for global dominance and influence.
Example: Allied Powers vs. Central Powers: WW1 saw the formation of two major alliances, the Allied Powers (including countries like France, Russia, and later the United States) and the Central Powers (including Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire).
Outbreak of Two World Wars: The inability to resolve conflicts and rivalries peacefully resulted in the outbreak of WW1 and later contributed to WW2.
Total War: WW1 was a "total war" involving the complete mobilization of resources by warring states, significantly impacting economies, and affecting civilian populations through bombings, famines, and epidemics.
Unprecedented Damage: The scale of destruction and casualties in WW1 surpassed previous wars, with civilians heavily affected alongside military personnel.
Global Scope: The battles of WW1 were fought in various regions, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Pacific, making it a truly global conflict.
Duration and Names: WW1 lasted from 28th July 1914 to 11th November 1918 and is known as the "Great War" or the "First World War."
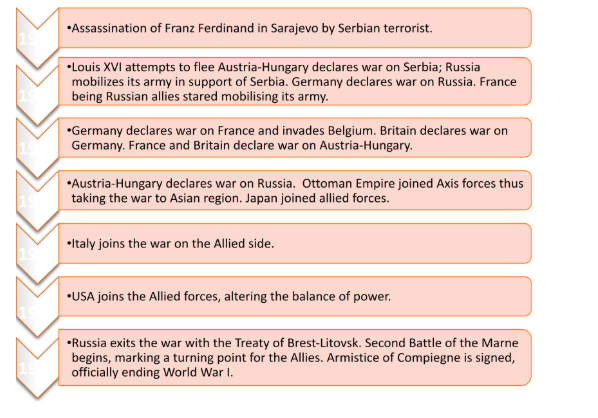
Timeline of World War I
Factors that led to World War I
Economic Factors
Industrialization: Industrialized nations sought colonies for raw materials and markets, leading to bitterness and rivalries.
Example: England, France, and Holland experienced it first, followed by Germany and Italy.
Imperialist Conquest: Asia and Africa were divided among imperialist countries, leading to conflicts and occasional wars.
Example: Russia's Ambitions led to clashes with Britain, Germany, and Austria over interests in Iran, the Ottoman Empire, and the Far East.
As an imperialist power, Japan sought expansion in the Far East, defeating Russia in 1904.
Market Competition: Germany's attempt to capture markets already controlled by Britain caused tension.
Tariff Wars: Countries imposed tariff restrictions, leading to worsened relations and trade conflicts.
Nationalism: Ambitions of Italy, France, Russia, and Japan clashed with other powers' interests.
Britain's Vast Empire: Defending its extensive empire caused Britain to be involved in conflicts with other imperialist countries.
Political Factors
Treaty of Frankfurt: Created enmity between Germany and France, leading to diplomatic isolation attempts by Germany.
Formation of Alliances: Defensive alliances and counter-alliances were formed among European powers.
Excessive Nationalism: Competitive patriotism fueled hatred and bitterness among nations.
Example: Italy and Germany's unification led to expansion at the expense of others' national sentiments.
Conflicts within Europe: The collapsing Ottoman rule in the Balkans fueled Pan-Slav and Pan-German movements, while Europeans engaged in secret treaties to acquire territories at the expense of other nations.
Example: Formation of Triple Alliance (Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy) and Triple Entente (France, Russia, and Britain).
Intellectual Factors
Thinkers’ contribution: War mentality encouraged by thinkers like Darwin, Spencer, Hegel, and Freud.
Example: Charles Darwin's theory of survival of the fittest led to a perception that the war eliminates the weak.
Immediate Cause
Assassination: The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary by a Serbian individual led to Austria-Hungary declaring war on Serbia
Immediate alliances: Russia joined the conflict to support Serbia. Germany, Austria-Hungary's ally, declared war on Russia due to their alliance commitment. Britain declared war on Germany because of Germany's invasion of neutral Belgium.
Consequences and aftermath of World War I
Rise of New Nations: Turkey, Austria, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, and Poland were created. Serbia formed Yugoslavia, and Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania became independent nations.
Terrible Loss of Life: The war resulted in eight million dead, millions wounded, and significant material destruction in Europe.
USA Emerged as a World Power: USA won the war without experiencing conflict on its territory, and USA became a major global power.
Women's Rights: Mass mobilization led to women's incorporation into the workforce, a significant step forward for women's rights.
Rise of Fascist Movements: Extreme nationalism and fear of Communist revolution led to the growth of fascist movements in some countries.
Russia Became Communist: The war contributed to the rise of Bolsheviks, leading to the Soviet Revolution and the spread of communist ideals.
League of Nations: Created as a diplomatic group to prevent conflicts, the League had mixed success in solving disputes.
Dismemberment of Ottoman Empire: The Ottoman Empire disintegrated after the war, and Turkey emerged as a new nation.
Disintegration of Habsburg Empire: Austria-Hungary separated, leading to the end of the Habsburg Empire.
Social Consequences: Birth rates declined, civilians lost land, and millions of young men died, leaving widows and orphans.
Introduction of New Weapons: World War I saw the first use of barbed wires, machine guns, tanks, poison gas, and shelling, making future wars more dangerous.
Imperialism Continued: German colonies became mandates, distributed among the victors for eventual independence. Ottoman Empire territories were handed over to France and Britain as mandates.
Economic Consequences: The war cost participating countries significantly, leading to inflation and economic challenges after the war.
Impact of World War I on India
Economic Impact
Losses: A huge rise in the defence expenditure of the British Colonial Government, which increased taxes on individual incomes and business profits
Business Profits: Indian business groups benefited from increased demand for industrial goods during the war, leading to substantial profits.
Resources: India supported the Allied powers with resources and manpower.
Example: Supplying food, raw materials, and troops to aid the war effort.
Social Impact
Recruitment of Indian Soldiers: Participating in battles in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East.
Example: Around 1.5 million Indian soldiers fought in the war.
Demographic Losses: India suffered significant population losses due to war-related causes.
Example: High casualties among soldiers and civilians, and famines.
Political Impact
Political Awakening: The war sparked increased nationalist sentiments and demands for self-governance.
Example: Growing discontent among Indians for not receiving substantial political reforms in return for their support during the war.
Montagu-Chelmsford Reforms: Some limited political reforms were introduced in 1919.Example: Expanding legislative councils and allowing greater Indian involvement in governance.
Emergence of Indian Nationalism: The war acted as a catalyst for the Indian nationalist movement.
Example: Leaders like Mahatma Gandhi and Jawaharlal Nehru advocated for independence and self-rule.
Khilafat Movement: Muslims expressed solidarity with their fellow Muslims globally.
Example: Demanding the protection of the Ottoman Caliphate and its leader's authority.
Tags:
History & Culture
Keywords:
WORLD WAR I
Great War
World war 1
1914 to 1918
Characteristics of World War I
Ultra Nationalism
Imperialism
Militarism
Allied Powers
Central Powers
France
Russia
USA
Germany
Austria-Hungary
and the Ottoman Empire
total war
Timeline of World War I
Franz Ferdinand
Sarajevo
Louis XVI
Belgium
Treaty of Brest Litovsk
Second Battle of the Marne
Armistice of Compiegne
Factors that led to World War I
Imperialist Conquest
Treaty of Frankfurt
Balkans
Pan-Slav and Pan-German movements
Triple Alliance
Triple Entente
Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Consequences and aftermath of World War I
Czechoslovakia
Poland
Bolsheviks
Habsburg Empire
Impact of World War I on India
Syllabus:
General Studies Paper 1
Topics:
World History
Related Articles
Mains Current Affairs
India-Russia
US Election Process - Comparison with India
NATO @75
Greenland, Panama, Canada: Why does Trump want it?
Prelims Current Affairs
Quadrilateral Security Dialogue(QSD)
The Five Eyes
BRICS
PUSA-2090
MQ - 9B Predator Drones
Dragon Drones
National Landslide Forecasting Centre(NLFC)
Mission Mausam Initiative
Pushpak Reusable Landing Vehicle (RLV) LEX 02
Pushpak RLV