INDIA AFRICA RELATIONS
Published on 27 Jan 2025
The story of India and Africa's partnership embodies an equal, consultative, and collaborative relationship. From the days of common struggle against colonialism to an evolving and multifaceted 21st century partnership under the framework of South-South Cooperation, the Africa-India partnership has come a long way.
Areas of Cooperation
✔ Political
● Historical Solidarity: India and African nations shared struggles for liberation, colonialism, and racial prejudice in the 20th century.
o Example: India supported Africa's democratic development and opposed apartheid at the United Nations.
● Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) and Ties: India built strong connections with African nations through the Non-Aligned Movement.
o Example: The political ties between both states are founded on principles of south-south cooperation, people-to-people linkages, and common developmental challenges.
● Peacekeeping and Security Collaboration: India actively participates in UN peacekeeping missions in Africa.
o Example: Indian soldiers are deployed in African peacekeeping missions, including Congo and South Sudan.
● Multilateral Engagement: India collaborates with African states on various international forums.
o Example: Cooperation in organisations such as IBSA and BRICS.
● Support for UN Aspirations: African states consistently support India's bid for a permanent seat in the UN Security Council.
● Institutionalized Relations: Since 2008, India-Africa relations have been formalized through the India-Africa Forum Summit (IAFS), with three such summits held to date.
✔ Economical
● Bilateral Trade Growth: India's bilateral trade with Africa reached US$ 89.5 billion in 2021-2022, a significant increase from US$ 56 billion the previous year.
● Trade Balance: India's exports to Africa constitute 5.2 percent of Africa's global imports, while India's imports from Africa make up 7 percent of the continent's global exports.
● Trading Partner: India is Africa's fourth-largest trading partner.
o Example: South Africa, Nigeria, Egypt, Kenya, Mozambique, and Tanzania are prominent destinations for India's exports to Africa.
Investments: India ranks among the top five investors in the African continent
o Example: Cumulative Indian investments in Africa between April 1996 and March 2022 amount to US$73.9 billion. Top investment destinations for India include Mauritius, Mozambique, Sudan, Egypt, and South Africa.
● Government Initiatives: Government supported initiatives have boosted bilateral trade and investment.
o Example: Initiatives like Focus Africa, TEAM-9, and the Duty-Free Tariff Preference Scheme
✔ Agriculture
● Promotion of Agribusiness in Africa by GoI: Government of India (GoI) promotes agribusiness in Africa.
o Example: Initiatives include Vocational Training Institutes, Agri-Business Incubation (ABI) Programme, and food-testing laboratories.
● Contract Farming Model: GoI has a contract farming model with Mozambique for importing 100,000 tonnes of pulses.
● Private sector efforts: Indian companies own 600,000 hectares of land in Africa for commercial farming, producing various crops for export to India.
o Example: Ethiopia is a preferred commercial farming destination for India. give subheading to each point
✔ Energy
● Diversification: India seeks to diversify its sources of oil away from the Middle East, and Africa can play a crucial role in India's energy supply.
o Example: Three of India's top four African trading partners (Nigeria, South Africa, Angola, and Algeria) are major oil producers.
● Oil imports: Africa currently accounts for around 16 percent of India's oil imports.
o Example: ONGC Videsh Limited's acquisition of a 25 percent stake in the Greater Nile Petroleum Operating Company.
● Uranium Imports from Africa: Potential for India to diversify its uranium imports from Africa, given that three African nations collectively hold eighteen percent of the world's uranium reserves.
o Example: Key uranium reserves in Niger (7 percent), Namibia (6 percent), and South Africa (5 percent).
● African Role in the International Solar Alliance (ISA):ISA, comprising 48 signatory countries, sees active participation from 25 African nations.
o Example: The ISA Secretariat is initiating large-scale solar projects of 500 MW each in multiple African countries.
✔ Infrastructure
Pan African e-Network Project: Information and Communications Technology (ICT) project between India and the African Union aims to connect the 55 member states of the African Union via a satellite and fiber-optic network.
o Example: Cumulative Indian investments in Africa between April 1996 and March 2022 amount to US$73.9 billion. Top investment destinations for India include Mauritius, Mozambique, Sudan, Egypt, and South Africa.
● Government Initiatives: Government supported initiatives have boosted bilateral trade and investment.
o Example: Initiatives like Focus Africa, TEAM-9, and the Duty-Free Tariff Preference Scheme
✔ Agriculture
● Promotion of Agribusiness in Africa by GoI: Government of India (GoI) promotes agribusiness in Africa.
o Example: Initiatives include Vocational Training Institutes, Agri-Business Incubation (ABI) Programme, and food-testing laboratories.
● Contract Farming Model: GoI has a contract farming model with Mozambique for importing 100,000 tonnes of pulses.
● Private sector efforts: Indian companies own 600,000 hectares of land in Africa for commercial farming, producing various crops for export to India.
o Example: Ethiopia is a preferred commercial farming destination for India. give subheading to each point
✔ Energy
● Diversification: India seeks to diversify its sources of oil away from the Middle East, and Africa can play a crucial role in India's energy supply.
o Example: Three of India's top four African trading partners (Nigeria, South Africa, Angola, and Algeria) are major oil producers.
● Oil imports: Africa currently accounts for around 16 percent of India's oil imports.
o Example: ONGC Videsh Limited's acquisition of a 25 percent stake in the Greater Nile Petroleum Operating Company.
● Uranium Imports from Africa: Potential for India to diversify its uranium imports from Africa, given that three African nations collectively hold eighteen percent of the world's uranium reserves.
o Example: Key uranium reserves in Niger (7 percent), Namibia (6 percent), and South Africa (5 percent).
● African Role in the International Solar Alliance (ISA):ISA, comprising 48 signatory countries, sees active participation from 25 African nations.
o Example: The ISA Secretariat is initiating large-scale solar projects of 500 MW each in multiple African countries.
✔ Infrastructure
● Asia-Africa Growth Corridor: Economic cooperation agreement between India and Japan.
● Pan African e-Network Project: Information and Communications Technology (ICT) project between India and the African Union aims to connect the 55 member states of of the African Union via a satellite and fiber-optic network.
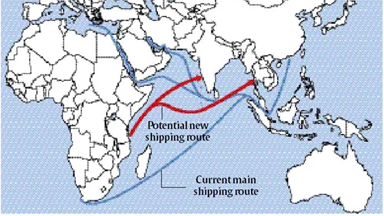
● Asia-Africa Growth Corridor: Economic cooperation agreement between India and Japan.
✔ Security
● Maritime security: India's defense relations with Africa based on "SAGAR," which stands for "Security and Growth for All in the Region."
o Example: Involves anti-piracy operations around the Gulf of Aden and providing security assistance to Indian Ocean Island states.
● Defense Initiatives: Multiple defence exercise have been held.
o Example: AFINDEX in 2019, the first-ever India-Africa Defense Ministers Conclave (IADMC) held in 2020. Proposal to establish the India-Africa Defense Dialogue as a regular event, coinciding with the biennial DefExpo military exhibition.
✔ Social
● Humanitarian Aid: India has supported Africa with multiple humanitarian aid.
o Example: Operation Vanilla 2020, Indian relief mission to aid Mozambique after Cyclone Diane.
● Healthcare Support: During the COVID-19 Pandemic India ensured the continuous supply of essential medical materials.
o Example: 'Vaccine Maitri' initiative: India supplied 24.7 million doses of COVID vaccines to African nations.
● Soft Power: Both countries share strong diaspora and cultural ties.
o Example: Over three million people of Indian origin in Africa.
● Education and training: 40% of training slots under the ITEC program allocated to African participants.
o Example: India offers approximately 50,000 scholarships to African students annually.
● Women empowerment: Tanzanian women trained in India for solar technology maintenance called 'Solar Mamas'.
o Example: Collaboration with Ethiopia and South Africa to empower women through the Kudumbashree movement, created by the Government of Kerala.
Challenges in India-Africa Relations
✔ Ethnic and Religious Conflicts: Ethnic and religious conflicts, along with governance problems in some African countries, deter Indian companies from venturing into the region.
✔ Terrorism and Violent Extremism: Terrorism and violent extremism pose a significant and growing threat to peace and security in Africa, affecting India's engagement.
✔ Growing Chinese Influence: China's increasing presence in Africa, backed by soft loans to African states, has expanded its influence on the continent, potentially overshadowing India.
✔ Land Leasing Controversies: Land leasing is a politically sensitive issue in Africa, with some Indian companies accused of land-grabbing and causing displacement without benefiting locals or enhancing food security.
✔ Racist Attacks on African Nationals: Recent racist attacks on African students in India have led to African nationals feeling unwelcome.
Way Forward
✔ Political Support: India can use its diplomatic influence to back African countries in their pursuit of peace, democracy, and development.
● Example: Advocate for African interests in global forums like the United Nations, G-20, and the World Trade Organization.
✔ Economic Partnership: Strengthen trade and investment ties by offering market access, preferential tariffs, and high-quality products and services.
✔ Knowledge sharing: Share best practices and experiences in areas like agriculture, rural development, microfinance, small and medium enterprises, and the digital economy.
● Example: Transfer Indian innovations, such as JAM (Jan Dhan-Aadhaar-Mobile), DBT (Direct Benefit Transfer), UPI (Unified Payments Interface), and Aspirational Districts Programme.
✔ Security Cooperation: Enhance security cooperation by providing training, equipment, and intelligence to African security forces.
✔ Science, Technology, and Innovation Collaboration: Promote science, technology, and innovation collaboration by supporting research and development projects in Africa.
✔ Cultural and Educational Exchange : Ensure the safety and welcoming environment for Africans studying or working in India.
● Example: Collaborate with Indian civil society organizations, NGOs, and institutions to implement cost-effective development projects in Africa.
The India-Africa relationship, anchored by the Kampala Principles, sets a powerful example of international collaboration. By strengthening their ties and adhering to these principles, India and Africa illustrate the potential for cross-continental cooperation and showcases the effectiveness of South-South Cooperation.
Tags:
World Affairs
Keywords:
Africa
South-South Cooperation
Kampala Principles
AFINDEX
SAGAR
Syllabus:
General Studies Paper 2
Topics:
International Relations
Related Articles
Mains Current Affairs
INDIA’S MINERAL PLAN IN AFRICA
Prelims Current Affairs
BRICS
The Underwater Structures in Indian Ocean named
Second Generation Distress Alert Transmitter (DAT-SG)
Bharat-Gen
Exercise La Perouse
Point Nemo
International Organization of Aids to Marine Navigation (IALA)
Bay of Bengal Inter-Governmental Organisation
Onchocerciasis
The Sagarmala Programme