Gaia Mission
Published on 07 Oct 2025
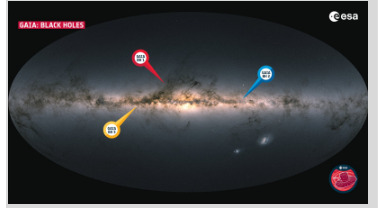
Astronomers have discovered a massive black hole, Gaia BH3, located about 2,000 light-years away in the constellation Aquila.
It is the third of its kind, following Gaia BH1 and BH2, all detected by the European Space Agency’s Gaia telescope.
Gaia, launched in 2013, aims to create the most precise 3D map of the Milky Way by tracking the motion of billions of stars.
Operating at the second Lagrange point, it observes each of its 1 billion target stars around 70 times over five years.
Gaia BH3 appears to be a passive black hole, not actively pulling in material from its surroundings.