WORLD WAR II
Published on 24 Oct 2025
World War II, spanning from 1939 to 1945, was a global conflict fueled by political tensions, territorial ambitions, and ideological clashes among major powers. It resulted in widespread destruction, the loss of over 70 million lives, and led to the emergence of the United States and the Soviet Union as superpowers, shaping the post-war geopolitical landscape and establishing the foundation for the Cold War.
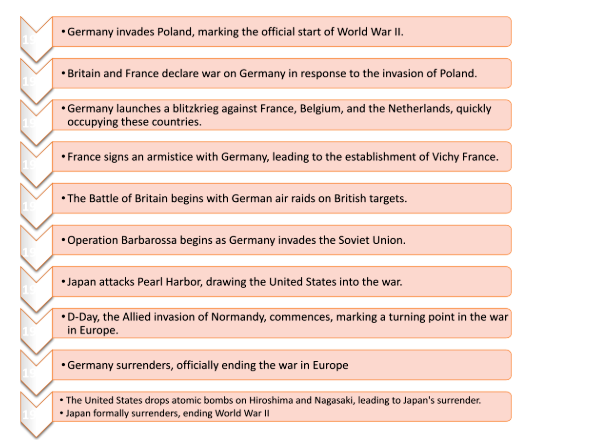
Timeline of World War II
Causes of World War II
Political Causes
Failure of the Treaty of Versailles: Harsh terms imposed on Germany after WWI led to political instability and resentment. Germany's loss of territories, colonies, and military restrictions fueled nationalist sentiments.
Failure of the League of Nations: Ineffective enforcement and lack of military power made the League unable to prevent aggressions.
Example: Italy's invasion of Ethiopia and Japan's invasion of Manchuria were not adequately addressed.
Rise of Hitler and Nazism: Adolf Hitler's charismatic leadership and promises to restore German pride appealed to the masses.
Example: Violation of the Treaty of Versailles, remilitarization, and expansionist policies escalated tensions.
Emergence of Japan: Imperial Japan’s expansionist policies and its rise as a powerful nation in the East threatened other nations.
Example: Japan's aggressive expansion by invading China and maneuvering to control a sphere of influence in the Pacific.
Failure of Appeasement Policy: The policy of appeasement failed to prevent Nazi aggression, leading to the outbreak of the Second World War.
Example: Hitler broke the Munich agreement by invading Czechoslovakia.
Economic Causes
Great Depression of 1929: Global economic crisis led to high unemployment and economic hardships. Desperation and frustration fueled support for extremist ideologies in some countries.
Germany’s Economic constraints: Germany's economic struggles due to reparations and loss of valuable resources. Hyperinflation and economic instability further weakened German society.
Social Causes
Nazism: Hitler's propaganda and scapegoating of minorities like Jews and others. Creation of a fervent nationalist and militaristic culture in Germany.
Mussolini and Fascism: Benito Mussolini's promise to revive the glory of ancient Rome resonated with Italians. Fascist ideologies created a sense of unity and purpose among Italians.
Conflict of Ideologies: Ideological divisions between democratic nations and authoritarian regimes. Nationalistic fervour and belief in superiority led to aggression and territorial ambitions.
The Treaty of Versailles was Dictated Peace
Exclusion of Germany: Germany was not allowed to participate in the negotiations. They could only express their views through writing, and their criticisms were disregarded.
Disarmament of Germany: The treaty imposed severe disarmament measures on Germany, rendering it virtually impotent to protect its law and order
War Guilt Clause: Although multiple countries were responsible for World War I, the War Guilt Clause solely imposed blame on Germany and its allies, exacerbating feelings of injustice and resentment.
Loss of Colonies: Germany's African colonies were taken away and converted into Mandates under the League of Nations, diminishing its global influence and resources.
War Reparations: The massive war reparations of 6600 million pounds imposed on Germany resulted in humiliation and economic hardship. It aimed to keep Germany economically weak for the foreseeable future.
Territorial Losses: Austria and Hungary were significantly reduced in territory and population, with most of Austria's industrial wealth transferred to Czechoslovakia and Poland leading to economic crises
The Treaty of Versailles' harsh terms and the perceived injustice it inflicted on Germany contributed to feelings of anger and resentment, ultimately fueling the rise of Adolf Hitler and Nazism in Germany, which played a significant role in the outbreak of World War II.
Impact of World War II
Widespread Destruction
Devastation: Over 40 million people were killed, with half of them being Russians. Destruction of German industrial areas and cities.
Holocaust: The systematic execution of six million Jews in concentration camps.
Atomic bombings: The bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki caused massive casualties and long-term health effects.
Decolonization
Start of decolonization: Britain and France faced domestic and external problems after the war, leading to the end of colonialism in Africa and Asia.
Independence movements: Colonies sought independence, resulting in the decolonization process.
Example: India gaining independence from British rule in 1947 and the partition of British India into India and Pakistan
Balance of Power
Decline of Europe: European domination diminished, and the balance of power shifted towards the USSR and the US.
Bipolarity: The US emerged as an economic powerhouse. The post-war world became a bipolar world with the US and the USSR locked in a Cold War rivalry.
Example: The Marshall Plan, providing economic aid to Western Europe, and the Berlin Airlift during the blockade of West Berlin by the Soviets.
"Third World" Emerged: These are countries that were non-aligned with the US-led Western bloc or the USSR-led Eastern bloc.
Birth of UN (United Nations)
International Peace: The United Nations Organization was established with its Charter aiming to promote lasting peace and international cooperation among nations.
Cold War
Start of Cold War: The Potsdam Conference resulted in disagreement between the Western Allies and the Soviet Union.
Example: Germany was divided into East Germany (Communist) and West Germany (democratic), leading to the Cold War.
Example: The Berlin Wall erected in 1961 by East Germany to prevent East Germans from fleeing to the West, and the Cuban Missile Crisis of 1962, a tense standoff between the US and the USSR over nuclear weapons in Cuba.
Impact of World War II on India
Economic Strain: India's economy was heavily affected due to disruptions in trade and industries during the war.
Example: India's industries were directed to produce war-related goods, causing shortages of consumer goods like cloth and food items.
Indian National Movement: The war provided an opportunity for the Indian National Congress to demand complete independence from British rule.
Example: "Quit India Movement" in 1942 intensified the demand for immediate independence.
Recruitment and Contributions: Indian soldiers played a crucial role in the war effort, with over 2.5 million joining the British Indian Army.
Crippling Finances: India's financial resources were drained to support the British war effort, aggravating the country's economic challenges.
Social Impact: The war led to disruptions in normal life, affecting education, healthcare, and agricultural productivity.
Example: The Bengal Famine of 1943, exacerbated by wartime policies, caused millions of deaths in India.
Strain on Unity: India's participation in the war exposed the divide between different religious and communal factions.
Example: Non-participation of CPI, Muslim League in the Quit India Movement
The war's end brought about the emergence of two superpowers, the United States and the Soviet Union, leading to the beginning of the Cold War and shaping the geopolitical landscape for decades to come. Additionally, the war's devastating toll on human lives and infrastructure underscored the urgent need for international cooperation, culminating in the formation of the United Nations to promote peace and prevent future global conflicts.
Tags:
History & Culture
Keywords:
WORLD WAR II
World war 2
1939 to 1945
United States and the Soviet Union
USA
USSR
cold war
Timeline of World War II
Germany
Poland
Britain
france
blitzkrieg
Belgium
Netherlands
armistice
Vichy France
Battle of Britain
peration Barbarossa
Pearl Harbor
Hiroshima and Nagasaki
Normandy
Treaty of Versailles
league of nationsm
Hitler
Nazi
Manchuria
Japan
Appeasement Policy
Munich agreement
Czechoslovakia
Great Depression of 1929
Mussolini and Fascism
Austria
Hungary
Impact of World War II
Holocaust
Atom bomb
Decolonization
Independence movements
Marshall Plan
United Nations
UN
Third World
Berlin Wall
Impact of World War II on India
Quit India Movement
Syllabus:
General Studies Paper 1
Topics:
World History
Related Articles
Mains Current Affairs
India’s Prevention of Money Laundering Act
Climate Engineering
Right Against Climate change impacts
Freshwater Quest
NTA Controversy and New Act
Zero Hunger
US Election Process - Comparison with India
NATO @75
PALESTINE IN UN
Israel and Hamas in International Criminal Court
Prelims Current Affairs
UN led conference on Afghanistan
Living Planet Report 2024
Blue line
United Nations’ Refugee Agency for Palestinians (UNRWA)
79th United Nations General Assembly
Central Emergency Response Fund (CERF)
United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon (UNIFIL)
Financing for Sustainable Development Report 2024
Group of Friends
Military Gender Advocate of the Year Award