INDIA USA RELATIONS
Published on 22 Jan 2025
Former US President Barak Obama had called the Indo-US relationship the ‘most defining’ partnership of the 21st century.
Historical Ties
✔ Post-Independence Challenges (1947-1960s)
● India was importing wheat from the US under Public Law 480 (PL480), also termed the “Food for Peace” programme.
● India faced war with Pakistan, and the US aligned with Pakistan, did not fully support India.
● India advocated for the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM), criticizing US intervention in Vietnam.
✔ The 1971 Turning Point (1971)
● India supported Bangladesh's formation, straining relations with the US.
● India shifted to closer ties with the Soviet Union, while the US enhanced relations with Pakistan.
✔ Nuclear Tests and Sanctions (1974)
● Operation Smiling Buddha, India's nuclear tests led to US restrictions on loans and economic assistance.
✔ 1980s: Afghan Conflict (1980s)
● Closer US-Pakistan ties to counter the Soviet Union raised India's security concerns.
✔ Post-Cold War Engagement (1990s)
● India provided limited support during the Gulf War.
● Economic liberalization facilitated closer ties, but CTBT pressure persisted.
● Flourishing Relationship (2000-2008)
● President Clinton's visit marked a new phase.
● Civil nuclear pact in 2008 was a significant milestone.
Areas of Cooperation
✔ Strategic
● US-India Civil Nuclear Deal (2006): Recognized India as a responsible nuclear power despite not signing the NPT. Secured a waiver for India at the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG), enabling civilian nuclear cooperation.
● Major Defense Partner: Designated India as a "Major Defense Partner," and elevating India to
Strategic Trade Authorization List (STA), allowing advanced technology imports.
● India-US 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue: Involves defense and foreign ministers, fostering closer cooperation on various fronts.
● QUAD (Quadrilateral Security Dialogue): A strategic forum with the US, India, Japan, and Australia, focusing on Indo-Pacific stability and shared values.
● Common Indo-Pacific Vision: Emphasizes regional sovereignty and autonomy, with India as a key player.
o Example: Renaming of the US Pacific Command as Indo-Pacific Command underscores India's importance.
● Counter-Terrorism Cooperation: A joint effort to combat terrorism through intelligence sharing and law enforcement collaboration.
o Example: India-US Counter-Terrorism Cooperation Initiative
✔ Security
● Arms trade: US is now India's second-largest arms provider.
o Example: India bought C-17 Globemaster-III, P-8A Poseidon , C130J Super Hercules, MH-60 Romeo helicopters etc from US defence manufacturing companies like Lockheed Martin and Boeing.
● Military Exercises: India conducts more bilateral exercises with the U.S. than with any other country.
o Example: Tiger Triumph, Malabar Exercise
● Foundational agreements: Agreements to enhance military cooperation and interoperability were signed.
o Example: BECA, COMCASA, LEMOA, GSOMIA
✔ Economic
● Trade Expansion: Bilateral trade between India and the US has surged, increasing tenfold since 2000.
o Example: The US holds the position of India's largest trading partner.
● Trade Surplus: India enjoys a trade surplus with the US, a unique aspect of their economic relationship.
o Example: In the fiscal year 2021-22, India recorded a substantial trade surplus of USD 32.8 billion with the US.
✔ Energy
● Comprehensive Energy Collaboration: Cooperation spans various aspects, including oil, natural gas, coal, power generation, energy efficiency, new technologies, renewable energy, and civil nuclear energy.
o Example: PEACE, initiated in 2015, is a part of the Partnership to Advance Clean Energy (PACE) and focuses on expanding access to clean energy.
● Crude Oil and Hydrocarbons: The US has become India's sixth-largest source of crude oil imports and hydrocarbons, enhancing India's energy security.
● Nuclear: India and the U.S. have a Civil Nuclear Energy Working group on R&D activities, and has ongoing projects under R&D collaboration
o Example: In 2020, India and the US extended their MOU for cooperation on Global Centre for Nuclear Energy Partnership (GCNEP) by 10 years.
✔ Diaspora
● Economic and Educational Excellence: Indian-Americans outperform other Asian American groups and the general US population, both economically and academically.
● Higher Education Impact: The number of Indian students pursuing US higher education has tripled in a decade, contributing to knowledge transfer and skill development in India.
● Advocacy for India: Groups like USINPAC and Friends of India actively advocate for India's interests and have achieved significant milestones.
o Example: Lobbying for the India-US Nuclear Deal in 2008.
✔ Others
● Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI): US is a part of CDRI which focuses on resilient infrastructure.
● Water Resource Management: MoU between India's Ministry of Jal Shakti and the US Geological Survey.
● Space Situational Awareness (SSA): Collaboration for space debris and traffic management to ensure safety for space assets.
● Young Innovators Internship Programme (YIIP): Creates science and economy internship opportunities for young entrepreneurs.
● Parliamentary Exchange and Judicial Cooperation: Facilitates reciprocal visits by Parliamentarians.
|
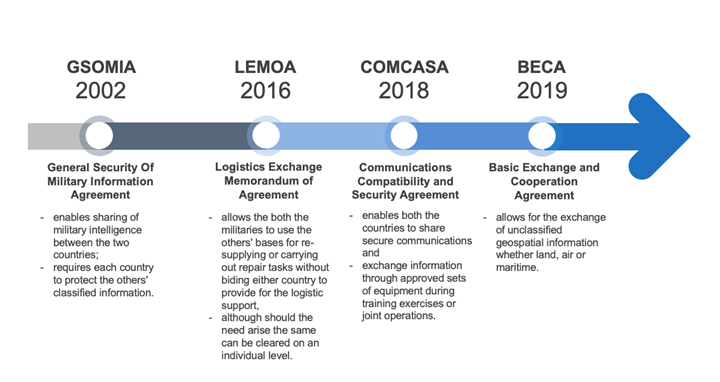
Foundational agreements between India and USA
✔ General Security of Military Information Agreement (GSOMIA): ● Allows sharing of classified technology and facilitates US weapons sales to India. ✔ Logistics Exchange Memorandum of Agreement (LEMOA): ● Covers port calls, joint exercises, training, and humanitarian assistance and facilitates Navy-to-Navy cooperation. ● Allows India to use US facilities globally for logistical support. ✔ Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement (COMCASA): ● Focuses on secure military communication. ● Enhances communications interoperability between the Indian and US militaries. ✔ Basic Exchange and Cooperation Agreement (BECA): ● Facilitates expanded geospatial information sharing between the armed forces. ● Enhances the accuracy of Indian missiles and armed drones through shared information. Impact of these agreements on India-US Relations ✔ These agreements signify a new level of trust and cooperation between the two countries. ✔ India and the US, both democracies with shared interests, deepen their cooperation in defense, particularly in the face of common threats. ✔ They are a response to the growing challenges posed by China's assertiveness in the region and globally. Advantages of these agreements for India ✔ India will emerge as a serious military power in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) due to these agreements. ✔ Institutionalization of these agreements makes their use more seamless. ✔ They facilitate cost-savings in procuring and maintaining US-made military systems and reduce logistical challenges. ✔ BECA allows India to closely monitor Chinese naval activities in the Indian Ocean. Concerns Raised ✔ Some experts express concerns about these agreements compromising India's strategic autonomy. ✔ It's important for India to balance its defense relationships and not overshadow its traditional ties, like those with Russia. ✔ Critics argue that these agreements primarily benefit the US, particularly LEMOA, as Indian ships are less likely to refuel and resupply at US ports. ✔ Some see these agreements as driven by the US's economic interests, including boosting arms sales to India. ✔ Implementation of COMCASA may pose challenges, given the prevalence of Russian-origin platforms in India's military. |
Challenges in India US relations
✔ Geopolitical
● Autonomous Foreign Policy: India’s autonomy affected by US’s foreign policies.
o Example: US sanctions, particularly CAATSA, have affected India's autonomy in foreign policy, creating challenges in arms purchases and energy trade.
● Afghanistan Peace Deal: The deal has implications for India's strategic interests in the region, potentially affecting its stakes in Afghanistan.
● US Withdrawal from Multilateralism: Unstable policies with respect to international organisations affecting multilateral cooperation.
o Example: The Trump administration's actions, such as leaving the Paris Climate Agreement, withholding funds from UNESCO but Biden administration rejoining the Paris Climate Agreement
● Obstruction in Global Organizations: The US has been an obstacle to reform in various global organizations.
o Example: USA is against the expansion of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) and IMF voting share reforms.
● Non-Aligned Position: India maintains a non-aligned stance regarding the Russian-Ukraine war, refraining from aligning with the American perspective.
o Example: India's import of affordable Russian oil continues to reach record levels, despite pressure to reduce such imports.
● Kashmir Issue: Pakistan has sought US engagement on the Kashmir issue, attempting to internationalize it but India maintains that Kashmir is a bilateral matter.
● US Adversaries: India's Engagement with US adversaries is affecting the ties.
o Example: India has criticized the US decision to block Iranian and Venezuelan oil from the global market. India also actively worked to bring Iran into the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO).
✔ Economic
● Trade Imbalance: The US has expressed concerns about the trade deficit with India.
● Unilateral Trade actions: US policies that affects India’s competitive advantage.
o Example: GSP Withdrawal and "Developed" Status: The US withdrew Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) benefits for certain Indian products and was removed from the list of "developing" countries, impacting trade actions that can be taken by the US.
● E-commerce Policies: India's data localization policies, including mandates for personal data storage within India, have raised concerns.
o Example: E-commerce regulations targeting foreign-owned platforms like Amazon have created tensions.
● Tariff Disputes: India has been labeled a "tariff king" by the US due to its high import duties.
o Example: Disputes over import tariffs on American motorcycles like Harley-Davidson persist.
● Intellectual Property (IP) Disputes: Differences exist in IP protection, especially concerning compulsory licensing and patent evergreening.
o Example: India's IP regime has been a concern for the US and has led to its placement on the "Special 301" Priority Watch List.
● Agricultural Trade Barriers: Sanitary and phytosanitary (SPS) barriers in India have limited US agricultural exports.
● Atmanirbhar Bharat Campaign: India's self-reliance campaign has raised concerns in the US that India is increasingly adopting protectionist policies and becoming a closed-market economy.
Way Forward
✔ Strategic Multi-Alignment: India must navigate the Ukraine-Russia conflict carefully, balancing its interests between Russia and the US.
✔ Leveraging Common Interests: The India-US defense partnership can create a more balanced Asia, reducing vulnerability to dominance by any single power like China.
✔ Economic Engagement: Both countries should work towards a FTA.
✔ Sustainable Development: Deepening clean energy cooperation can help both nations achieve climate goals while promoting economic growth. E.g. cooperation between ISA and PACE.
✔ Engaging Private Sectors: Many companies are diversifying supply chains away from China. India can signal readiness to become a hub for chip manufacturing with US assistance.
✔ Bilateral ties: Strengthening bilateral trade ties and platforms like the 'Quad' can facilitate the creation of alternative supply chains
The Ending of US Hegemony and the Rise of Asia
According to McKinsey Global Institute, Asia could generate more than half of the world’s GDP by 2040 as cross-border flows shift toward the region, which is rapidly integrating; with 60% of goods traded, 56% of greenfield foreign direct investment (FDI) and 74% of journeys by Asian air travelers taking place within the region. This reflects the changing waves from the west to Asia.
Decline of US
✔ Economic Decline: The shifting of manufacturing bases to countries like China has led to a relative decline in the economic power of the U.S.
✔ Wars: The financial costs of military engagements have been substantial, contributing to economic challenges affecting the U.S.'s global standing.
● Example: Wars in Iraq and Afghanistan
✔ Failure of Institutions: International institutions like the WTO and IMF, dominated by the U.S., have faced challenges and a lack of leadership in addressing global issues. Meanwhile, Asia has seen the emergence of new multilateral initiatives.
● Example: Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB), BRICS New Development Bank (NDB), Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), etc.
✔ Diplomacy Failure: The withdrawal from important international institutions like UNESCO has weakened American diplomacy and its influence on multinational agreements.
● Example: Rise of BRICS, SCO etc.
✔ Rise of Middle-East Asia: Regional powers in the Middle East, such as Iran and Turkey, have become increasingly assertive and independent, challenging U.S. influence in the region.
✔ Decline in America's Image: During the Trump era, U.S. policies and actions have eroded its global image and leadership.
● Example: US’s threat to withdraw from NATO, withdrawing from the Paris Agreement on climate change, and controversial immigration policies.
✔ Shift from Democratic Values: Concerns have arisen about the U.S. moving away from its traditional advocacy for democratic values and international cooperation.
● Example: Ultra-nationalism and a focus on ethnic purity in some policy discussions have raised questions about the U.S.'s commitment to these principles.
Rise of Asia
✔ Economic
● Economic Ascendancy: Asia has witnessed significant economic growth, with countries like China and India becoming major global economic players.
o Example: China's rapid economic expansion has made it the world's second-largest economy, challenging the US's economic dominance.
● Trade and Investment: Asian countries have become hubs for trade and investment, attracting businesses and capital from around the world.
o Example: The ASEAN region has become a focal point for foreign direct investment and manufacturing, reducing reliance on the US.
✔ Technology and Defence
● Technological Advancements: Asian nations are at the forefront of technological innovation, particularly in areas like electronics, artificial intelligence, and biotechnology.
o Example: South Korea's Samsung and China's Huawei are global leaders in the smartphone industry, challenging US tech giants.
● Military Modernization: Asian countries have been investing in modernizing their military capabilities, increasing their regional influence.
o Example: China's military expansion and assertiveness in the South China Sea have shifted the regional military balance.
✔ Geopolitical
● Diplomatic Initiatives: Asian nations are actively engaging in diplomacy and forging alliances to shape global affairs.
o Example: The Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad) involving India, Japan, Australia, and the US aims to promote a free and open Indo-Pacific, countering China's influence.
● Multilateral Organizations: Asia is home to influential multilateral organizations, such as ASEAN, which play vital roles in regional stability and cooperation.
o Example: ASEAN has facilitated diplomatic dialogues and conflict resolution in Southeast Asia.
✔ Social
● Soft Power: Asian cultures, media, and soft power have gained global popularity, shaping global perceptions.
o Example: The global reach of Japanese anime, South Korean K-pop music, and Bollywood films showcases Asia's cultural influence.
● Regional Integration: Asian nations are increasingly integrating economically and politically, creating regional blocs and cooperation frameworks.
o Example: BRI, BBIN, TAPI etc
● Climate Change: Asian countries have assumed leadership roles in addressing global challenges, such as climate change.
o Example: India is a global leader in climate change initiatives like ISA, CDRI.
● Global Demographic Shift: Asia's large and youthful population provides a demographic advantage, contributing to its economic dynamism.
o Example: India's young and growing workforce is seen as a demographic dividend, attracting global businesses.
|
Opportunities for India ✔ Global Supply Chain Hub: India can become a major sourcing base for global supply chains. ● Example: It could aim to capture a 15-20% share of the $500 billion global mobile handset market by reducing reliance on imports. ✔ Attracting Investments: India can attract more investments from Asian countries. ● Example: Softbank has invested in Indian startups, but there's potential to secure more investments from across Asia by strengthening ties with other countries. ✔ Innovation Hub: India can tap into the innovation boom in East Asia. ● Example: Collaborating with Asian nations in sectors like electric mobility, 5G telecom, and renewable energy can help Indian firms become part of the global innovation landscape. |
India-US relation remains critical for the shaping of world order in the 21st century. In order to realise the full potential of relations, the two governments must now strive to complete the unfinished agreements and set the course for a Comprehensive Strategic Global Partnership.
Tags:
World Affairs
Keywords:
USA
QUAD
2+2 DIALOGUE
CIVIL NUCLEAR DEAL
BECA
Syllabus:
General Studies Paper 2
Topics:
International Relations
Related Articles
Mains Current Affairs
US Election Process - Comparison with India
NATO @75
Greenland, Panama, Canada: Why does Trump want it?
Prelims Current Affairs
Quadrilateral Security Dialogue(QSD)
The Five Eyes
PUSA-2090
MQ - 9B Predator Drones
National Landslide Forecasting Centre(NLFC)
Mission Mausam Initiative
Pushpak Reusable Landing Vehicle (RLV) LEX 02
Pushpak RLV
PMECRG & MAHA-EV Mission
Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technology (iCET)