INDIA BANGLADESH RELATIONS
Published on 08 Jan 2025
The people of India and Bangladesh share close and
multi-faceted socio-cultural, religious
and linguistic ties spanning centuries. The two countries share the same
values of secularism, pluralism and democracy.
Why is Bangladesh important to India?
ü Political
· Strategic Stability: Bangladesh
is vital for regional stability in South Asia.
· Border Relations: India shares a 4,096 km border with
Bangladesh.
· Counter-China Concerns: India
and Bangladesh can jointly address concerns regarding China.
o
Example:
Initiatives like OBOR can be countered.
ü Security
· Insurgent Activity Control: Bangladesh's
cooperation helps curb insurgent activities along the border, enhancing India's
Northeast security.
· Connectivity and Trade: The
border facilitates trade and connectivity, benefitting India's Northeastern
states.
ü Economic
· Northeast Connectivity: Bangladesh
provides a crucial land bridge to India's Northeast, ensuring uninterrupted
connectivity.
· Act East Policy: Bangladesh
serves as a bridge to Southeast Asia under India's Act East Policy.
Areas of Cooperation
ü Political
· Multilateral Engagement:
Both countries are committed to multilateralism and actively participate in
regional organizations such as SAARC, BIMSTEC, and IORA.
o
Example:
Bangladesh
plays a significant role in India's Neighbourhood First policy, emphasizing the
importance of regional cooperation.
· Support for International Reforms: Bangladesh
supports India's efforts to reform global institutions like the UN, WTO and
IMF.
o
Example:
The
country also endorses India's aspiration for a seat in the United Nations
Security Council (UNSC).
ü Economic
· Bilateral Trade:
Bangladesh is the 6th largest trade partner of India.
o
Example:
The Duty-Free and Quota-Free access provided by India under the South Asian
Free Trade Area (SAFTA) since 2011 is appreciated by Bangladesh.
o
The India-Bangladesh Border Haat serves as
a weekly border trade market, promoting commerce and acting as a reunion
spot for families residing on both sides.
· Special Economic Zones: Special
Economic Zones have been established in Bangladesh to accommodate Indian
manufacturing companies, enhancing economic cooperation.
· Financial Support: India has extended significant lines of credit
(LOCs) and grants to Bangladesh
o
Example:
Indian LOC and grants up
to $8 billion aimed at addressing economic disparities and fostering
development.
· Infrastructure and Capacity building:
India has significantly invested in Bangladesh's development.
o
Example:
Exim Bank provides substantial loans, approximately $4.5 billion, for financing
social and infrastructure projects in Bangladesh.
· Indian
Technical and Economic Cooperation: Capacity-building
programs under the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation initiative
contribute to strengthening people-to-people interactions.
o
Example:
India and Bangladesh have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) aimed at
sustainable development in Sylhet.
· Tourism: Bangladeshi
tourists constitute one of the largest groups visiting India, facilitated by a
more liberalized visa regime.
ü Energy
· Nuclear Power Collaboration: India
is actively engaged in Bangladesh's nuclear power program
o
Example:
India is assisting in the construction of the Rooppur nuclear power plant in
collaboration with Russia.
o
India has been providing training to
Bangladeshi nuclear scientists as part of this partnership.
· Power Export: India
is set to export electricity to address Bangladesh's energy deficit.
o
Example:
Adani Power has inked a long-term pact with Bangladesh Power Development Board
to supply electricity. Bangladesh signed an agreement to LPG to the Indian
state of Tripura.
o
The India-Bangladesh Friendship Product
Pipeline Project involves the construction of a 130-kilometre-long pipeline
connecting Siliguri in West Bengal to Parbatipur Bangladesh, to supply refined
diesel.
ü Connectivity
· Inland Waterways Trade:
India and Bangladesh share 54 common rivers.
o
Example:
The Ganga Waters Treaty was signed in 1996 for the sharing of waters of river
Ganga during the lean season.
o
The Kushiyara Pact on the Kushiyara River
was signed that will benefit people in Southern Assam and the Sylhet region in
Bangladesh in 2022.
· Transport:
The Kolkata-Dhaka-Agartala Bus Service, launched in 2015, significantly reduced
travel distances.
o
Example:
The Maitree Express train service connects Dhaka in Bangladesh to Kolkata.
o
BBIN was signed to facilitate the movement
of passenger and cargo vehicles across borders.
o
Agartala-Akhaura Rail-Link will be the
first rail route between Northeast India and Bangladesh.
ü Social
· Cooperation in Health Sciences: Both
countries have signed a MOU on health and medical sciences, including joint
research and the exchange of doctors and health professionals.
· COVID-19 Assistance: India
has provided medical relief assistance to Bangladesh as part of its support to
SAARC countries during the COVID-19 pandemic.
o
Example:
Bangladesh
was one of the highest recipients of vaccines from India.
· Medical Tourism: Bangladesh
accounts for over 35% of India's international medical patients, reflecting
strong healthcare cooperation.
· Scholarships and Skill Development: Bangladeshi
students receive scholarships from the Indian Council for Cultural Research
(ICCR) annually.
o
Example:
India offers financial support to children of freedom fighters in Bangladesh
through the 'Muktijodha scholarship' scheme.
ü Defence
· Joint Exercises: Regular
joint army exercises, are conducted between the Indian and Bangladeshi armies.
o
Example:
SAMPRITI
· Border Security Collaboration:
BSF and Border Guards Bangladesh (BGB) participated in the 'Mainamati Maitree
Exercise' to enhance joint operational efficiency and border management.
o
Example:
India has extended a line of credit worth US$500 million to Bangladesh for the
purchase of defence equipment.
· Surveillance and Equipment: MoU
for the establishment of a Coastal Surveillance Radar System in Bangladesh was
signed, enhancing coastal security.
o
Example:
Bangladesh
has extradited many "most wanted" criminals to India, strengthening
security cooperation.
ü Cultural
· Shared Heritage: Both
countries share the distinction of having their national anthems written by
Rabindranath Tagore.
· Cultural Centres: Cultural collaborations
to enhance soft power.
o Example: The Prime Minister of both countries inaugurated Bangladesh Bhawan at Vishwa Bharti University in Santiniketan, West Bengal, which will house a museum and library, further enhancing cultural ties.
Challenges in India - Bangladesh Relations
✔ Political
●
Big Brother Attitude: Bangladesh sometimes views India
as displaying a "big brother" attitude in the region, which can
strain relations.
● Rohingya Crisis: Bangladesh has expressed dissatisfaction with India's handling of the Rohingya refugee crisis.
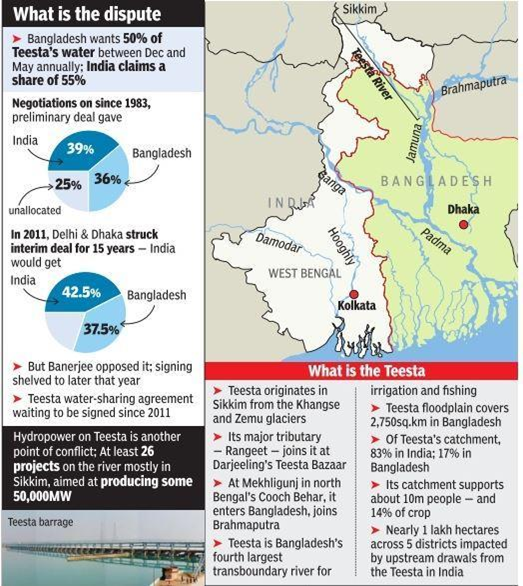
● Water Sharing Disputes: Bangladesh has concerns regarding the equitable sharing of water from 54 transboundary rivers.
o Example: Teesta River- Bangladesh is heavily dependent on the Teesta River, with 73% of its population relying on it for livelihood.
o Example: Construction of the Farakka Barrage has reduced the availability of water for irrigation and industry in Bangladesh, leading to upstream-downstream issues.
✔ Security
● Border Issues: The presence of illegal migrants along the India-Bangladesh border has led to changes in demography and ecological concerns in India's northeastern states.
● Insurgency: The rise of insurgent groups like the Assam Gana Sangram Parishad in the border regions adds security challenges.
● Smuggling: The smuggling of currency, drugs, medicines, and livestock across the border has been a persistent issue.
● Border Shootings: 2020 witnessed the highest number of border shootings by the Border Security Force (BSF), adding tension to border relations.
✔ Economy
● Trade Disputes: Bangladesh seeks India's cooperation in reducing non-tariff barriers to further facilitate trade.
o Example: Non-tariff barriers may include stringent quality standards, sanitary and phytosanitary measures, and complex customs procedures.
|
China Factor: China’s deepening relations with Bangladesh is a matter of concern for India ✔ China is Bangladesh's largest trading partner making it heavily reliant on China. ✔ Bangladesh actively participates in the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), a Chinese-led infrastructure and economic development project that India has not joined. ✔ Bangladesh is the second-largest recipient of Chinese loans in South Asia after Pakistan, with China committing US$28 billion in lines of credit for various infrastructure development projects. ✔ China is developing a 750-acre industrial park in Bangladesh, primarily for use by Chinese manufacturing firms. The park is located in the main port city of Chittagong. ✔ Both China and Bangladesh have plans to construct a 900 km highway connecting Chittagong and Kunming (Yunnan) through Myanmar. This highway project would enhance trade, people-to-people contact, and grant Bangladesh access to the Mekong sub-region. ✔ Bangladesh heavily relies on military hardware from China, a matter of concern for India. ✔ China has managed to maintain a consensus among political parties in Bangladesh through its 'apolitical' image. |
Way Forward
✔ Water Sharing Challenges: India and Bangladesh must address water-sharing challenges collaboratively, focusing on negotiations to find solutions, such as the Teesta River dispute.
✔ Branding Assistance: India can enhance its diplomatic efforts by effectively branding its development assistance to Bangladesh, fostering a positive image among the Bangladeshi people.
✔ Institutionalized Security Cooperation: Both countries should institutionalize security cooperation to ensure its continuity beyond specific governments, promoting long-term stability and trust.
✔ Visa Regime Liberalization: Simplifying visa procedures can encourage tourism, business exchanges, and cultural interactions between India and Bangladesh.
✔ Investment in Bangladeshi Businesses: India can boost economic ties through trade delegations and participation in trade fairs, promoting bilateral trade and economic cooperation.
✔ India's Regional Influence: Amid competition from China, India should adapt its foreign policy to maintain and strengthen its influence in the South Asian region.
✔ Energy Security: In response to the growing global energy crisis, India and Bangladesh should cooperate on adopting clean and sustainable energy sources to achieve energy self-sufficiency in South Asia.
✔ Focus on Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA): As Bangladesh transitions from an LDC to a developing country by 2026, the CEPA can help manage this shift while strengthening economic ties between India and Bangladesh.
✔ Addressing the Refugee Crisis: India and Bangladesh can lead efforts in SAARC to establish a declaration on refugees, outlining clear procedures for determining refugee status and handling economic migration issues.
India-Bangladesh relations have gained positive momentum over the last decade, with India remaining a key neighbour and strategic partner. Both nations should continue working together to deepen their cooperation.
Tags:
Polity
Keywords:
Bangladesh
BIMSTEC
SAARC
Act East Policy
Teesta
Syllabus:
General Studies Paper 2
Topics:
India and Its Neighbors
Related Articles
Mains Current Affairs
INDIA- BANGLADESH RELATIONS
Prelims Current Affairs
South Asia SubRegional Economic Cooperation (SASEC)
2nd BIMSTEC Foreign Ministers Retreat
Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project (KMTTP)
Teesta River
Free Movement Regime
Kopili & Kushiyara Rivers
Bay of Bengal Inter-Governmental Organisation
Ganga Water Treaty (GWT)
1972 Shimla Agreement