INDIA AFGHANISTAN RELATIONS
Published on 19 Dec 2024
India and Afghanistan share a robust bond rooted in their historical and cultural connections. India has played a pivotal role in the reconstruction and recovery of Afghanistan, with the Strategic Partnership Agreement further solidifying their dynamic, multifaceted relationship.
Historical Ties
ü Ancient Heritage: Gandhara, part of modern-day Afghanistan, was one of the 16 Mahajanapadas in Vedic India.
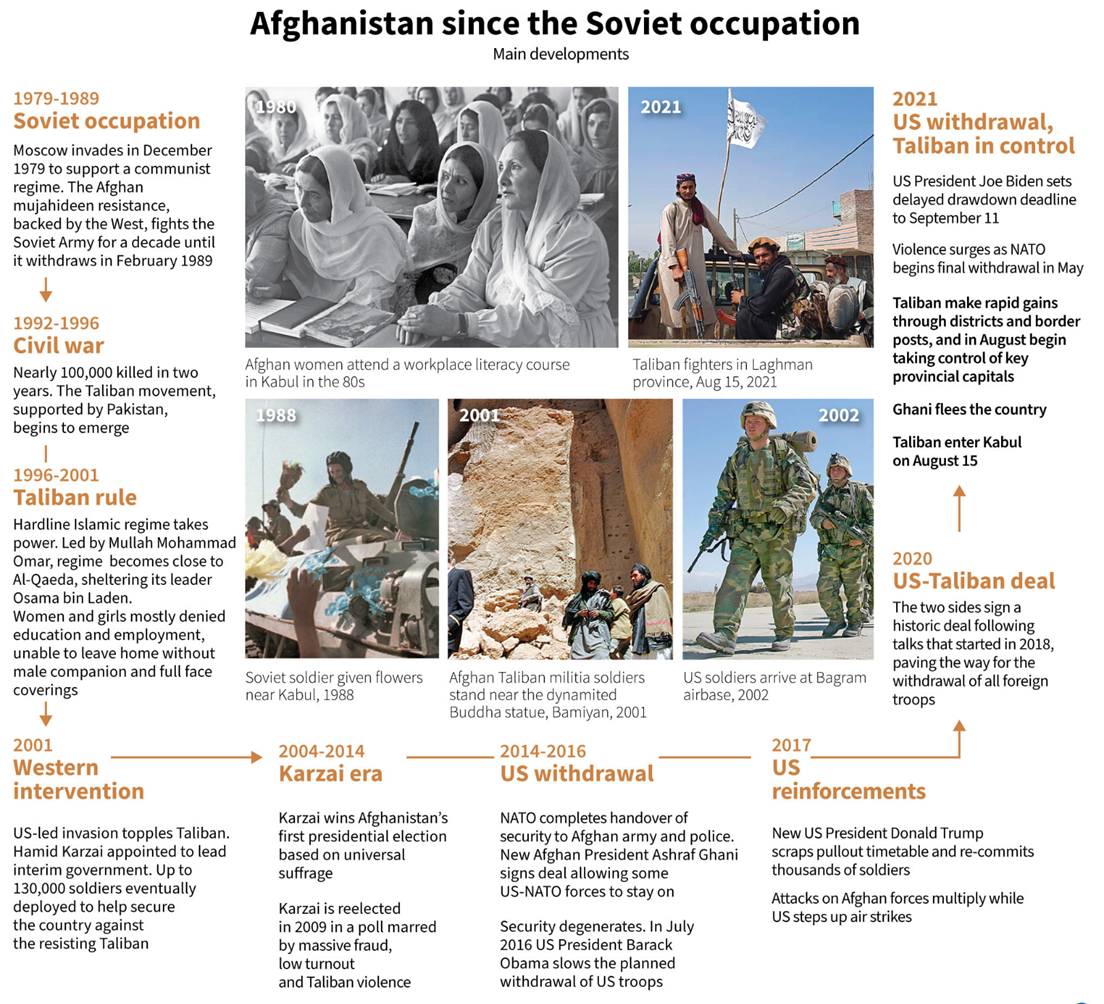
ü Soviet Intervention (1979-89): India was the sole South Asian nation to recognize the Soviet-backed Democratic Republic of Afghanistan during the Soviet intervention.
ü Regional Cooperation: In 2005, India proposed Afghanistan's membership in SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation).
ü Strategic Partnership Agreement (2011): India and Afghanistan signed a Strategic Partnership Agreement in 2011, strengthening their bilateral relations.
ü Recent Developments: After the Taliban takeover in Afghanistan, the Indian Armed Forces initiated "Operation Devi Shakti" to evacuate Indian citizens and foreign nationals following the fall of Kabul.
ü India- Taliban relations:
· India and the Taliban have a contentious history due to incidents like the IC-814 hijacking in 1999, which led to the release of terrorists responsible for attacks on Indian soil.
· The Taliban perceived India as hostile due to its support for anti-Taliban forces after the 9/11 attacks.
· India never diplomatically recognized the Taliban during their rule from 1996-2001.
· India has adjusted its stance, recognizing the Taliban's role in Afghan peace talks, and is now engaging with them in discussions and agreements, indicating a notable shift.
Why is Afghanistan important to India?
ü
· Connectivity: Afghanistan is pivotal for India's connectivity to Eurasia, ensuring energy security.
o Example: The TAPI Pipeline
· Gateway to Central Asia: Afghanistan serves as a crucial gateway for India to access landlocked Central Asian countries, fostering trade and economic connections Security and Stability.
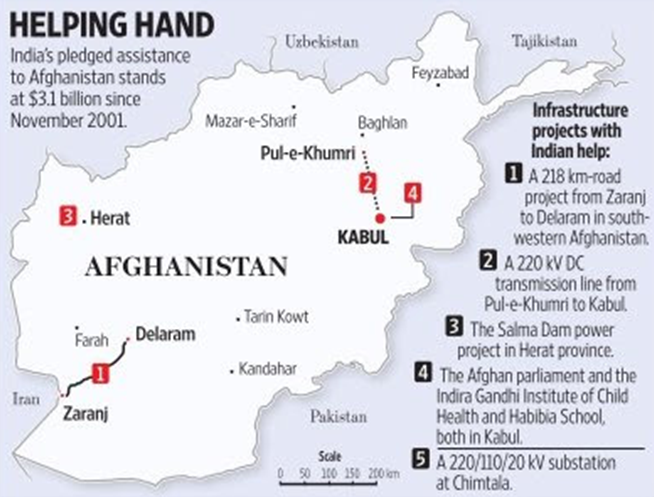
· Indian Investments: Since 2001, India has committed USD 3 billion towards rebuilding and reconstruction of Afghanistan.
o Example: Indian investments in infrastructural projects like The Afghan Parliament, Salma Dam, Zaranj- Delaram Highway, etc.
· Trade Potential: The prospect of trade with Afghanistan, along with Central Asian nations and Iran, holds the potential for India to achieve an annual trade volume of $500 billion.
o Example: The Chabahar Port will allow trade with Afghanistan and Iran, bypassing Pakistan.
· Abundant Resources: Afghanistan is rich in resource deposits, estimated to be worth trillions of dollars, as per the US Geological Survey.
· Trade Relations: Despite the absence of direct land access, India stands as the second-largest destination for Afghan exports, reflecting the robust trade ties between the two nations.
· Indian Business Presence: Several Indian companies are actively engaged in business activities in Afghanistan, contributing to economic partnerships and development.
o Example: Companies like Gammon India, Phoenix, and APTECH.
ü Internal Security
· Countering Radical Ideology: Afghanistan's significance lies in countering radical ideology, drug trafficking, and smuggling impacting India's internal security.
· Kashmir Security: Stability in Afghanistan is integral to India's security interests, especially in the Kashmir region and prevents illicit drug trade proceeds from the Golden Crescent.
ü Geopolitical Significance
· Location: Afghanistan's strategic location remains vital for India, especially given the complex India-Pakistan relations.
Areas of Cooperation
ü Political
· SAARC Inclusion: India's push for Afghanistan's inclusion in SAARC in 2005, ultimately realized in 2007, aimed at fostering peace and regional security.
· Strategic Partnership Agreement: The 2011 agreement further strengthened India-Afghanistan ties through various initiatives.
ü Economic
· Indian investments: India has invested over USD 3 billion in Afghanistan, fostering its soft power.
o Example India constructed Afghanistan's Parliament complex and the Indo-Afghan Friendship Dam.
· MoUs for Infrastructure: In 2019, India signed 11 MoUs worth $9.5 million with Afghanistan for various infrastructure and public service projects.
ü Social
· Medical Support: India has equipped Afghan medical facilities and provided modern medical equipment.
· Agriculture University: India played a crucial role in establishing Afghanistan's first agriculture university in Kandahar.
· Scholarships and Training: India sponsors annual university and short-term training programs, benefiting Afghan students and public servants.
· Medical Tourism: India is a preferred destination for Afghan medical tourists, reflecting trust in its healthcare system.
ü Humanitarian Assistance
· Funding and Services: India contributes funds to the Afghan Red Crescent Society, offers free medical services, and deploys technical advisers.
· Vocational Training: Vocational courses are provided for Afghan youth, particularly women.
o Example: Tele-Education: India supports Afghan education through tele-education courses.
Challenges in India- Afghan Relations
ü Political
· Taliban: Historically strained relations with the Taliban have made the post-Taliban engagement process tricky for India.
· Pakistan Factor: Pakistan has actively attempted to hinder India's efforts to strengthen its relationship with Afghanistan.
o Example: Taliban-ISI Nexus are raising concerns for India
· Increasing Chinese Presence: India is wary of China's expanding role in Afghanistan and its engagement with the Taliban
o Example: The absence of U.S. financial and military aid opens doors for China to gain influence in the region.
ü Security
· Shared Terror Threat: India and Afghanistan are both targeted by terrorism, with groups like Al-Qaeda operating in Afghanistan posing significant concerns for India.
· Opium Production: Afghanistan's status as the world's largest opium producer contributes to regional instability and violence, affecting both India and Afghanistan. It is also part of Golden crescent countries(Afghanistan, Iran and Pakistan)
ü Economic
· Indian Investments: Afghanistan's economic and infrastructural woes, compounded by security issues and corruption, have impeded India's investments
o Example: Projects such as the Salma Dam and Parliament Building.
Way Forward
ü Broadening International Engagements: Beyond isolating the Taliban, India now faces diminishing returns as more countries engage with the group, necessitating a shift in its approach.
ü Enhancing National Security: Engagement with the Taliban offers India an opportunity to express concerns about terrorist ties, such as those with Lashkar-e-Taiba and Jaish-e-Mohammed.
ü Mutual Benefits: The Taliban's gestures, including encouraging India to reopen its mission in Kabul and resuming direct flights, demonstrate potential for mutually beneficial cooperation.
ü Comprehensive Strategic Approach: India requires a holistic, long-term strategy for Afghanistan, encompassing political, economic, military, and diplomatic dimensions, within the framework of a grand strategy.
ü Clear Strategic Goals: India's Afghan policy should be based on a clear understanding of its strategic objectives in the region, taking into account the global and regional strategic landscape.
ü Improved Diplomatic and Economic Ties: Both India and the Taliban must consider each other's concerns, aiming to enhance diplomatic and economic relations.
ü Increased Investment: India should amplify its investments in Afghanistan, particularly in areas like infrastructure, agriculture, and energy, thereby bolstering the Afghan economy, creating jobs, and deepening economic ties.
India should reassess its Afghanistan engagement in light of shifting regional dynamics and establish a multilateral humanitarian aid corridor, involving grassroots civil society for aid accountability. The Indian government allocating ₹200 crore to Afghanistan in the 2023-24 budget, shows a positive step towards reigniting the ties with Afghanistan.
Tags:
Polity
Keywords:
Afghanistan
Taliban
SAARC
TAPI
Operation Devi Shakti
Syllabus:
General Studies Paper 2
Topics:
India and Its Neighbors
Related Articles
Mains Current Affairs
India Taliban relations
Prelims Current Affairs
UN led conference on Afghanistan
Bay of Bengal Inter-Governmental Organisation
Torkham Border Crossing
Taliban Sanctions Committee & 1373 Counter-Terrorism Committee